Application difference of methyl cellulose (MC), hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)
2021-12-06After the refined cotton is treated with alkali, chlorinated methane is used as an etherifying agent, and a series of reactions are carried out to produce cellulose ether. Generally, the degree of substitution is 1.6~2.0, and the solubility varies with the degree of substitution. Belongs to non-ionic cellulose ether.
(1) Methyl cellulose is soluble in cold water, and it is difficult to dissolve in hot water. Its aqueous solution is very stable in the range of pH=3~12. It has good compatibility with starch, guar gum, etc. and many surfactants. When the temperature reaches the gelation temperature, gelation will occur.
(2) The water retention of methyl cellulose depends on its added amount, viscosity, particle fineness and dissolution rate. Generally, if the added amount is large, the fineness is small, and the viscosity is large, the water retention rate is high. Among them, the addition amount has the greatest impact on the water retention rate, and the viscosity is high
Low is not proportional to the level of water retention. The dissolution rate mainly depends on the degree of surface modification of the cellulose particles and the fineness of the particles. Among the above cellulose ethers, methyl cellulose and hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose have higher water retention rates.
(3) The change of temperature will seriously affect the water retention rate of methyl cellulose. Generally, the higher the temperature, the worse the water retention. If the temperature of the mortar exceeds 40℃, the water retention of methyl cellulose will be significantly worsened, which will seriously affect the workability of the mortar.
(4) Methyl cellulose has a significant effect on the workability and adhesion of the mortar. The "adhesion" here refers to the adhesive force felt between the worker's application tool and the wall substrate, that is, the shear resistance of the mortar. The adhesion is large, the shear resistance of the mortar is large, and the force required by the workers in the use process is also large, and the workability of the mortar is poor. In cellulose ether products, the adhesion of methyl cellulose is at a medium level.
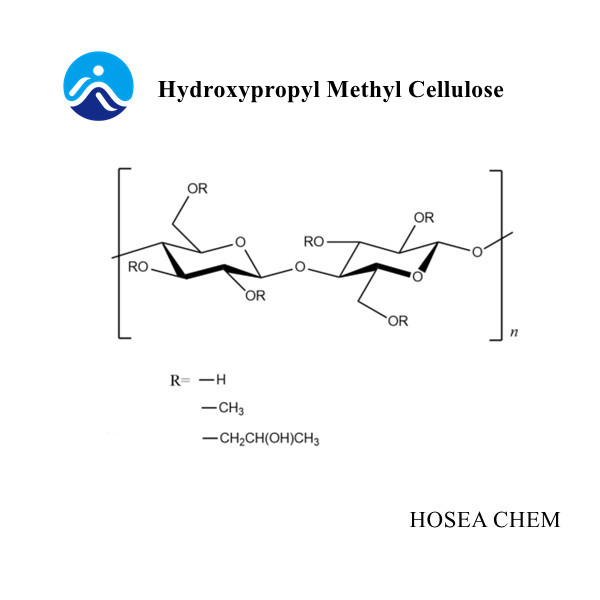
2. Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC)
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose is a cellulose variety whose output and consumption have been increasing rapidly in recent years. It is a non-ionic cellulose mixed ether made by a series of reactions using propylene oxide and methyl chloride as etherifying agent after alkalization of refined cotton. The degree of substitution is generally 1.2 to 2.0. Its properties are different by the ratio of methoxy content and hydroxypropyl content.
(1) Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose is easily soluble in cold water, and it will be difficult to dissolve in hot water. But its gelation temperature in hot water is significantly higher than that of methyl cellulose. The dissolution in cold water is also greatly improved compared to methyl cellulose.
(2) The viscosity of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose is related to its molecular weight, and the higher the molecular weight, the higher the viscosity. Temperature also affects its viscosity, as the temperature increases, the viscosity decreases. But its high viscosity has a lower temperature effect than methyl cellulose. The solution is stable when stored at room temperature.
(3) The water retention of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose depends on its addition amount, viscosity, etc. The water retention rate under the same addition amount is higher than that of methyl cellulose.
(4) Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose is stable to acid and alkali, and its aqueous solution is very stable in the range of pH=2~12. Caustic soda and lime water do not have much effect on its performance, but alkali can accelerate its dissolution rate.
And to improve the viscosity of the pin. Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose is stable to general salts, but when the concentration of the salt solution is high, the viscosity of the hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose solution tends to increase.
(5) Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose can be mixed with water-soluble polymer compounds to form a uniform and higher viscosity solution. Such as polyvinyl alcohol, starch ether, vegetable glue and so on.
(6) Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose has better enzyme resistance than methylcellulose, and its enzymatic degradation possibility in solution is lower than that of methylcellulose.
(7) The adhesion of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose to mortar construction is higher than that of methyl cellulose.
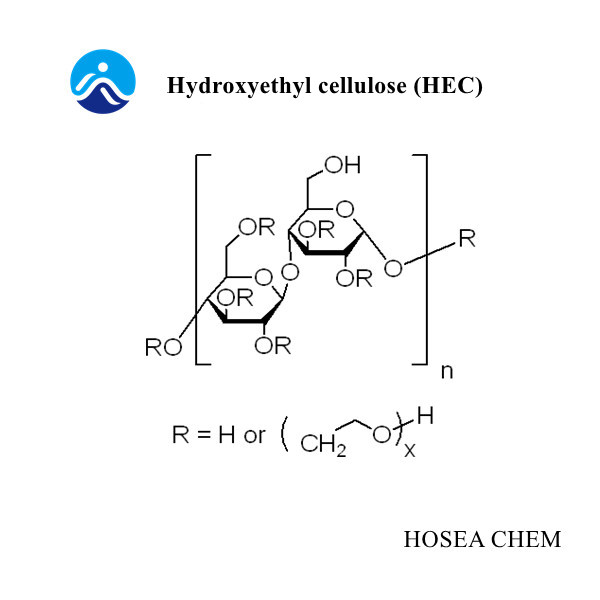
3. Hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC)
After the refined cotton is alkali-treated, it is made by reacting with ethylene oxide as an etherifying agent in the presence of acetone. The degree of substitution is generally 1.5 to 2.0. It has strong hydrophilicity and is easy to absorb moisture.
(1) Hydroxyethyl cellulose is soluble in cold water, but it is difficult to dissolve in hot water. Its solution is stable at high temperature and does not have gelling properties. The mortar can be used for a long time at high temperature, but its water retention is lower than that of methyl cellulose.
(2) Hydroxyethyl cellulose is stable to general acids and alkalis. Alkali can accelerate its dissolution and slightly increase its viscosity. Its dispersibility in water is slightly worse than that of methyl cellulose and hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose. .
(3) Hydroxyethyl cellulose has good anti-sagging properties for mortar, but has a longer retardation time for cement.
(4) The performance of hydroxyethyl cellulose produced by some domestic enterprises is significantly lower than that of methyl cellulose due to its high water content and high ash content.
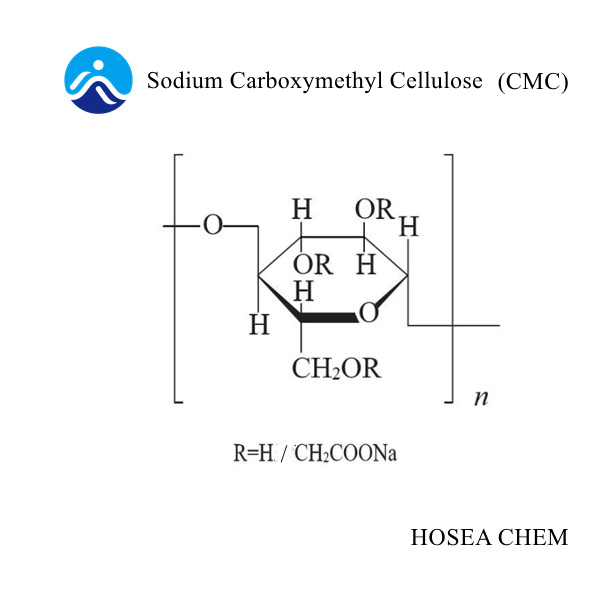
4. Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)
After being alkali-treated from natural fibers (cotton, etc.), sodium monochloroacetate is used as an etherifying agent and a series of reaction treatments are used to make ionic cellulose ethers. The degree of substitution is generally 0.4 to 1.4, and its performance is greatly affected by the degree of substitution.
(1) Carboxymethyl cellulose is highly hygroscopic, and it will contain a lot of water when stored under normal conditions.
(2) The carboxymethyl cellulose aqueous solution does not produce gel, and the viscosity decreases with the increase of temperature. When the temperature exceeds 50℃, the viscosity is irreversible.
(3) Its stability is greatly affected by pH. Generally it can be used in gypsum-based mortar, but not in cement-based mortar. When it is highly alkaline, it loses its viscosity.
(4) Its water retention is much lower than that of methyl cellulose. It has a retarding effect on gypsum-based mortar and reduces its strength. But the price of carboxymethyl cellulose is significantly lower than that of methyl cellulose.
The application difference of methyl cellulose (MC), hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC), carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), methyl cellulose (MC), hydroxypropyl The application difference of methyl cellulose (HPMC), hydroxyethyl cellulose (HEC) and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) methyl cellulose (MC), hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose (HPMC), hydroxyethyl Application difference between cellulose (HEC) and carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC)