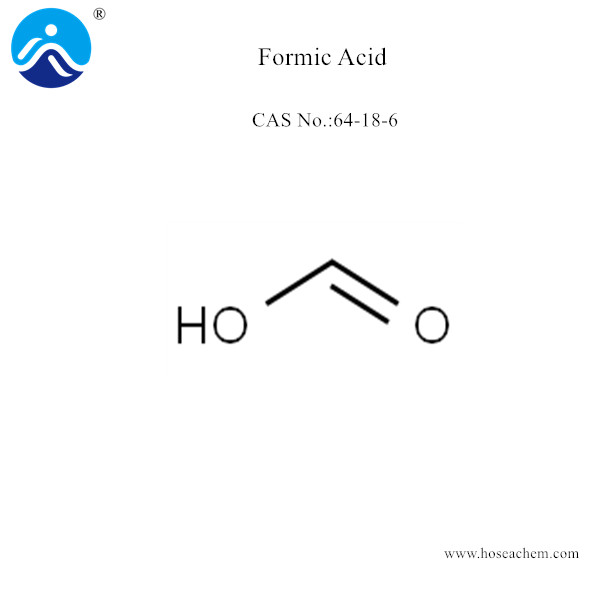
Formic Acid
Hosea Chem® has been supplying Formic Acid (CAS 64-18-6) with high quality and competitive price for many years, covering most of the European, American, etc. Send Inquiry
Product Description
Formic Acid
Chemical Name:Formic Acid;CAS 64-18-6
EINECS No.: 200-579-1
Chemical Formula: CH2O2
Molecular Weight: 46.03
Melting point: 8.2-8.4°C
Boiling point: 100-101℃
Flash point: 133°F
Density at 25°C: 1.22 g/mL
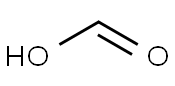
Molecular Structure:
Description
Formic acid is a colorless liquid having a highly pungent, penetrating odor at room temperature. It is miscible with water and most polar organic solvents, and is somewhat soluble in hydrocarbons. In hydrocarbons and in the vapor phase, it consists of hydrogen-bonded dimers rather than individual molecules . Owing to its tendency to hydrogen - bond, gaseous formic acid does not obey the ideal gas law. Solid formic acid (two polymorphs) consists of an effectively endless network of hydrogen - bonded formic acid molecules. This relatively complicated compound also forms a lowboiling azeotrope with water ( 22.4 % ) and liquid formic acid also tends to supercool.
Ethylene Carbonate Standard
Appearance: Colourless Liquid
Density at 25°C: 1.22 g/mL
Vapor pressure (37℃): 52mmHg
Refractive index n20/D: 1.377
Explosive limit %(v): 12-38
Application
A major use of formic acid is as a preservative and antibacterial agent in livestock feed. In Europe, it is applied on silage (including fresh hay) to promote the fermentation of lactic acid and to suppress the formation of butyric acid; it also allows fermentation to occur quickly, and at a lower temperature, reducing the loss of nutritional value. Formic acid arrests certain decay processes and causes the feed to retain its nutritive value longer, and so it is widely used to preserve winter feed for cattle. In the poultry industry, it is sometimes added to feed to kill E. coli bacteria . Use as preservative for silage and (other) animal feed constituted 30 % of the global consumption in 2009.
Formic acid is also significantly used in the production of leather, including tanning (23 % of the global consumption in 2009[7]), and in dyeing and finishing of textile (9 % of the global consumption in 2009 ) because of its acidic nature. Use as a coagulant in the production of rubber constituted in 2009 6 % of the global consumption.
Formic acid is also used in place of mineral acids for various cleaning products, such as limescale remover and toilet bowl cleaner. Some formate esters are artificial flavorings or perfumes. Beekeepers use formic acid as a miticide against the tracheal mite (Acarapis woodi) and the Varroa mite. The use of formic acid in fuel cells is also under investigation.
Storge & Handling
Shall be stored in a cool, dry place to maintain its stability and prolong its shelf life. Proper storage conditions are crucial to prevent product degradation, as ethylene carbonate can slowly decompose in the presence of moisture.
Packing
200KG/Drum