Ethylene Glycol (EG)
Hosea Chem® has been supplying Ethylene Glycol (EG) (CAS 107-21-1) with high quality and competitive price for many years, covering most of the European, American, etc. Send Inquiry
Product Description
Ethylene Glycol (EG)
Chemical Name:Ethylene Glycol;EG;CAS 107-21-1
EINECS No.: 203-473-3
Chemical Formula: C2H6O2
Molecular Weight: 62.07
Melting point: -13°C
Boiling point: 195-198℃
Flash point: 230°F
Density at 25°C: 1.113 g/mL
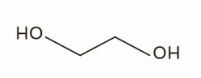
Molecular Structure:
Description
Ethylene glycol is a colorless, viscous, sweet liquid that is almost odorless at room temperature. It has a high boiling point and a low freezing point. It is used as an antifreeze and in coolants, detergents, paints, lacquers, pharmaceuticals, adhesives and cosmetics.
Ethylene Glycol Standard
Appearance: Colourless Transparent viscous liquid
Content %≥: 99.5
Density at 25°C: 1.113 g/mL
Vapor pressure (20℃): 0.08 mmHg
Refractive index n20/D: 1.431
Explosive limit %(v): 3.2
Application
Ethylene glycol is a versatile chemical compound with a wide range of industrial and commercial applications. Some of the primary uses of ethylene glycol include:
1. Antifreeze and coolant. Ethylene glycol plays a crucial role in automotive antifreeze and coolant, preventing engine overheating or freezing. It is able to interfere with thehydrogen bonds in water, making it difficult for the water molecules to bind.
2. Polyester resins and fibers. Ethylene glycol is mainly used in the production of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic resin. This resin is widely used to make soda, water and juice beverage containers.
3. Desiccant. Leveraging the hygroscopic nature and high boiling point of ethylene glycol, it emerges as an excellent desiccant and dehydrating agent.
While these are the main three uses of ethylene glycol, this chemical has a variety of applications that range across many industries. Ethylene glycol is also used in:
Hydraulic Fluids: It is employed as a hydraulic fluid in various applications due to its low viscosity and excellent thermal stability.
Heat Transfer Fluids: Ethylene glycol is used as a heat transfer fluid in applications such as solar water heaters and geothermal heating systems. It helps transfer heat efficiently.
Plasticizer: In certain plastic and polymer manufacturing processes, ethylene glycol can be used as a plasticizer, improving flexibility and workability.
Solvent: It serves as a solvent in the formulation of inks, dyes, and other chemical products. Its miscibility with water and many organic solvents makes it a versatile solvent.
Brake Fluids: Ethylene glycol is used in the formulation of brake fluids due to its high boiling point and hygroscopic (water-absorbing) nature, which helps maintain the fluid’s stability under varying conditions.
Natural Gas Hydrate Inhibitor: It is employed in the oil and gas industry as an inhibitor for the formation of natural gas hydrates, which can obstruct pipelines and equipment.
Preservatives in Wood: Ethylene glycol is used as a wood preservative to prevent wood from drying out, cracking, and shrinking.
Personal Care Products: It can be found in certain personal care products such as skin creams, lotions, and hair care products due to its humectant properties, helping to retain moisture.
Lab Use: Ethylene glycol is commonly used to extract proteins in solutions. It’s also used to preserve specimens in school labs, especially during dissection.
Storge & Handling
Shall be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight, heat, and ignition sources. Ensure proper ventilation and keep containers tightly closed when not in use.
Packing
230KG/Drum