Dimethylformamide (DMF)
Hosea Chem® has been supplying Dimethylformamide (DMF) (CAS 68-12-2) with high quality and competitive price for many years, covering most of the European, American, etc. Send Inquiry
Product Description
Dimethylformamide
Chemical Name:Butyl Acetate;DMF;CAS 68-12-2
EINECS No.: 200-679-5
Chemical Formula: C3H7NO
Molecular Weight:73.09
Melting point: -61°C
Boiling point: 153℃
Flash point: 136°F
Density at 25°C: 0.944g/mL
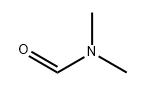
Molecular Structure:
Description
Dimethylformamide is a flammable, colorlessliquid with a fishy, unpleasant, amine-like odor at relativelylow concentrations. Soluble in water.Potential Exposure: Tumorigen,Mutagen; Reproductive Effector; Human Data; Hormone,Primary Irritant. DMFA is used as a solvent for liquids,gases, and as a gasoline additive. Dimethylformamide haspowerful solvent properties for a wide range of organiccompounds. Because of its physical properties, this chemical has been used when solvents with a slow rate of evaporation are required. It finds particular usage in themanufacture of polyacrylic fibers, butadiene, purified acetylene, pharmaceuticals, dyes, petroleum products, and otherorganic chemicals.
Butyl Acetate Standard
Appearance: Colorless liquid
Color APHA: ≤15
Color (APHA)≤: 10
Content %≥: 99.0
Density at 25°C: 0.944 g/mL
Vapor pressure (20℃): 2.7 mmHg
Refractive index n20/D: 1.430
Ignition point: 421 °C
Explosive limit %(V): 2.2-16
Application
It is a clear liquid that has been widely used in industries as a solvent, an additive, or an intermediate because of its extensive miscibility with water and most common organic solvents. Dimethylformamide solutions are used toprocess polymer fibers, films, and surface coatings; to permit easy spinning of acrylic fibers; to produce wire enamels, and as a crystallization medium in the pharmaceutical industry.
DMF can also be used for formylation with alkyllithium or Grignard reagents. It is used as a reagent in Bouveault aldehyde synthesis and also in Vilsmeier-Haack reaction. It acts as a catalyst in the synthesis of acyl chlorides. It is used for separating and refining crude from olefin gas. DMF along with methylene chloride acts as a remover of varnish or lacquers. It is also used in the manufacture of adhesives, fibers and films.
It is a solvent and used as an extractant, particularly for salts and compounds with high molecular mass. This role is consistent with its interesting combination of physical and chemical properties: low molecular mass, high dielectric constant, electron-donor characteristics, and ability to form complexes. The use of DMF as a component in synthesis is of relatively minor significance, at least commercially. N,N-Dimethylformamide (anhydrous) has been used as solvent for the synthesis of cytotoxic luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LH-RH) conjugate AN-152 (a chemotherapeutic drug) and fluorophore C625 [4-(N,N-diphenylamino)-4′-(6-O-hemiglutarate)hexylsulfinyl stilbene]. It may be employed as solvent medium for the various organic reduction reactions.
Storge & Handling
DMF should be stored in chemically resistant containers, typically made of stainless steel or certain types of plastic like polyethylene. The purified DMF is packaged for storage and distribution. It is typically stored in airtight containers to prevent moisture absorption and degradation.
Packing
190KG/Drum