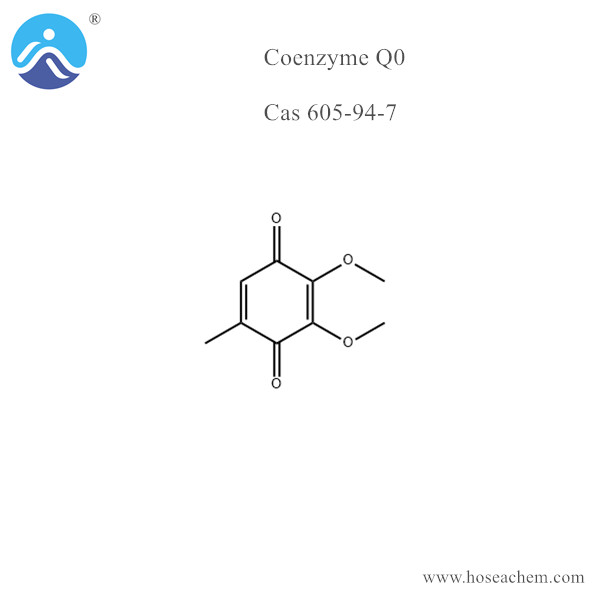
Coenzyme Q0
Hosea Chem® has been supplying Coenzyme Q0 (Cas 605-94-7) with high quality and competitive price for many years, covering most of the European, American, etc. Send Inquiry
Product Description
Coenzyme Q0
Chemical Name: Coenzyme Q0; CAS 605-94-7
EINECS No.: 210-100-8
Chemical Formula: C9H10O4
Molecular Weight: 182.17
Melting point: 58-60°C
Boiling point: 331.4±42.0 °C
Density: 1.19±0.1 g/cm3
Flash point: 148.6 °C
Molecular Structure:
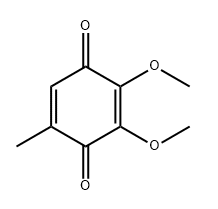
Description
2,3-Dimethoxy-5-methyl-p-benzoquinone, also known as coenzyme Q0, is a key intermediate in the synthesis of coenzyme Q, coenzyme Q10, other ubiquinones, and vitamin E.1,2 It inhibits the growth of SKOV-3, A2780, and A2870/CP70 human ovarian carcinoma cells (IC50s = 26.6, 27.3, and 28.4 µM, respectively) with a cytotoxic concentration of greater than 40 µM for non-cancerous ovarian surface epithelial cells.3 It halts the cell cycle at the G2/M phase, increases the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and induces autophagy and apoptosis in SKOV-3 cells. 2,3-Dimethoxy-5-methyl-p-benzoquinone downregulates the protooncogene HER-2 and decreases the protein levels of phosphorylated AKT and mTOR in SKOV-3 cells. It also decreases the incidence of tumors and tumor burden in a SKOV-3 human ovarian carcinoma mouse xenograft model when administered at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg every four days.
Coenzyme Q0 Standard
Appearance: red or orange crystals or fibres
Refractive Index: 1.498
Application
It is an important intermediate for the production of CoQ10, which has been used to treat many different conditions. There's evidence that CoQ10 supplements can lower blood pressure slightly.
Storge & Handling
Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area.
Packing
25KG/Drum