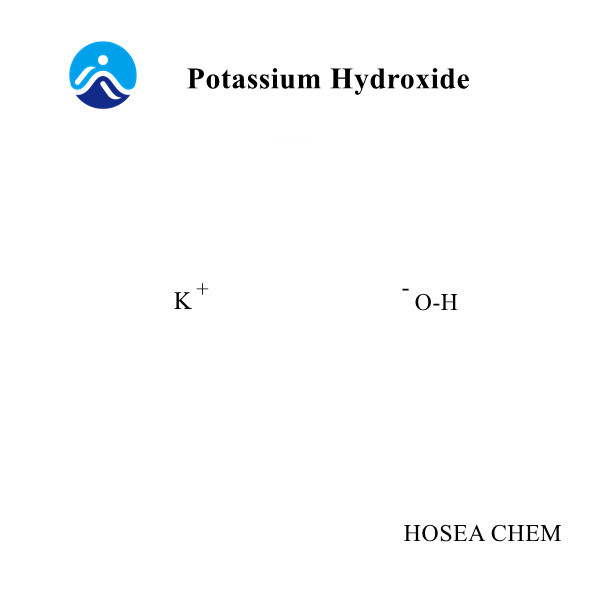
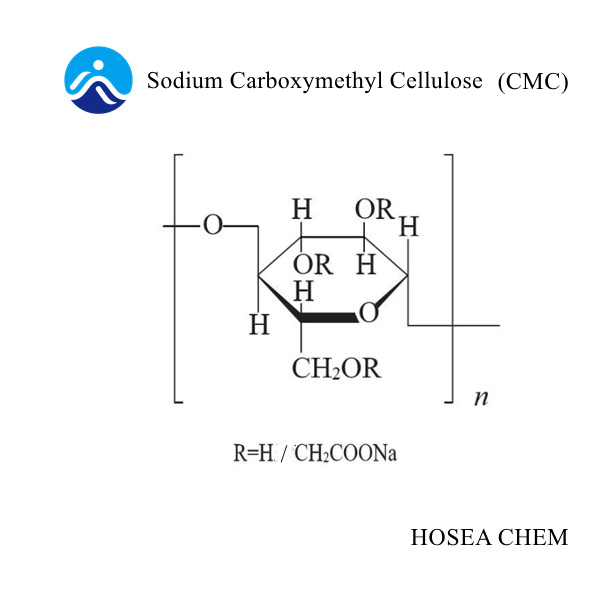
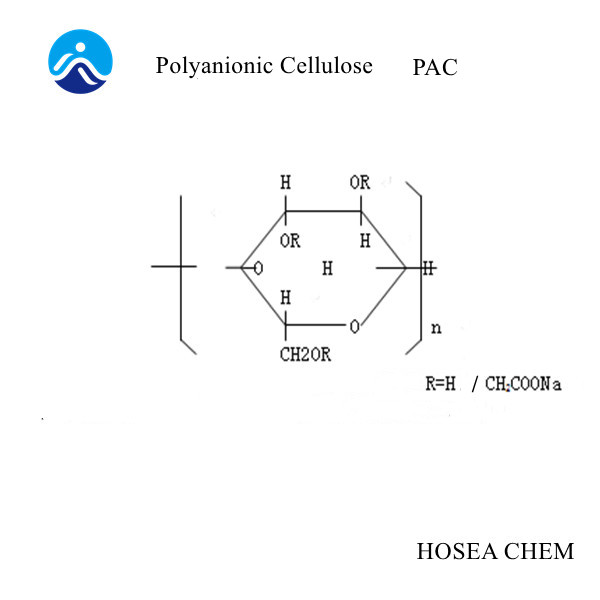
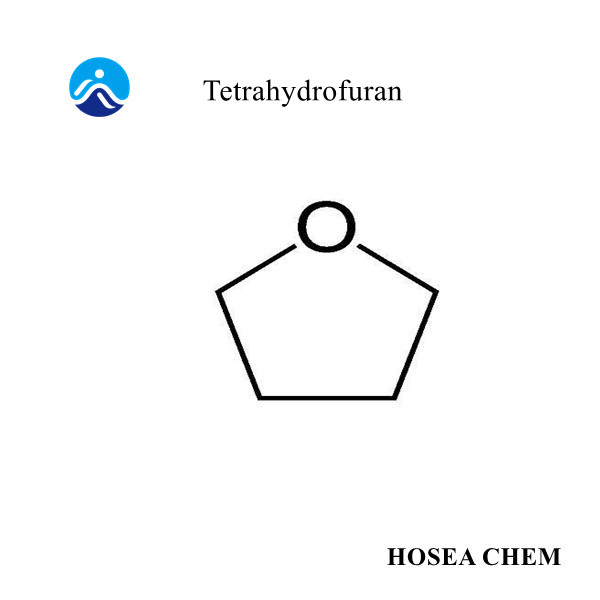
What are the uses of diphenylamine?
2024-11-09Diphenylamine is an important organic compound with a wide range of uses. For example:
1. In the field of rubber additives: it can be used to produce antioxidants, inhibitors, accelerators, etc.; it is also used as a rubber antioxidant. The produced antioxidant has good resistance to heat-oxygen and flex-cracking, has a certain protective effect on metal aging and ozone cracking, and has a light color, low toxicity, and low price.
2. As a dye intermediate: used to prepare azo dyes and other dyes, such as acid yellow G, acid orange N, acid ink blue A, disperse blue 5R, etc.
3. In the production of stabilizers: it can be used as an intermediate for plastic stabilizers, veterinary sulfonamides, and phenothiazines; it can also be used as a stabilizer for nitrocellulose and smokeless explosives.
4. As an analytical reagent: used for the identification of oxidizing substances such as nitrates and chlorates, catalytic determination of iridium, and photometric determination of nitrates; it can also be used as a redox indicator for the inspection or determination of oxides, and as a liquid desiccant.
5. Other uses: used in the pharmaceutical field to prepare phenothiazines, etc.; used in the agricultural chemical field to prepare other organic compounds, etc.; and can also be used as an additive for refining metals.
It should be noted that diphenylamine is toxic to a certain extent, irritating to the skin and mucous membranes, and can cause symptoms such as blood poisoning. When using and handling diphenylamine, relevant safety regulations should be observed and appropriate protective measures should be taken to avoid harm to the human body. At the same time, it is a regulated chemical. Individuals are not allowed to purchase it, and relevant units must also comply with corresponding regulations and requirements during purchase, storage, use, and transportation.