What is Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose (Sodium CMC )?
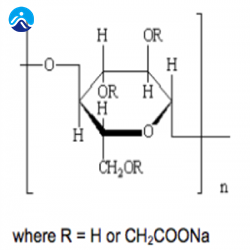
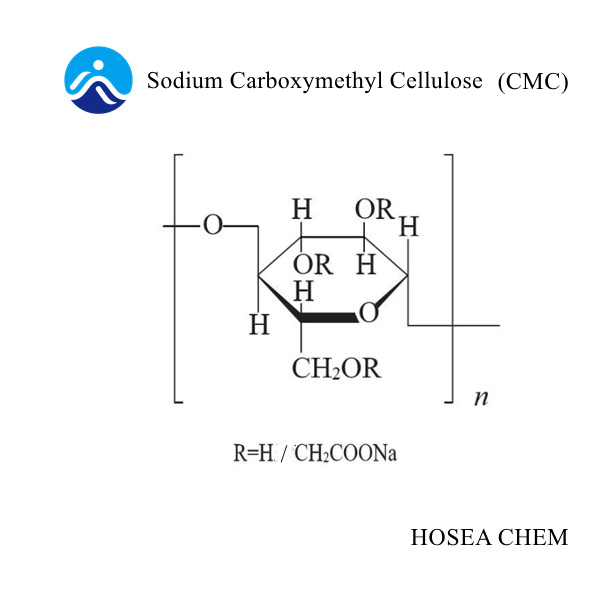
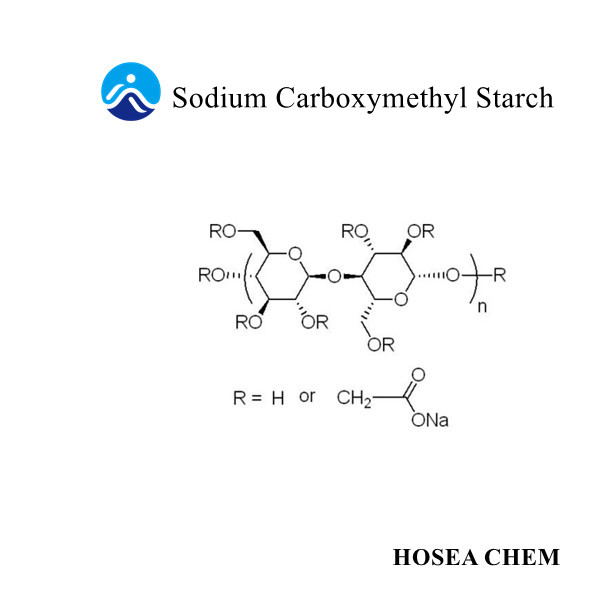
2021-11-06Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC sodium)is a multifunctional ingredient, which is composed of anhydroglucose units with an average of 0.2-1.5 carboxymethyl groups (-CH2COOH) on it, which can be used as a booster in foods. Thickener, binder, emulsifier and stabilizer, European food additive number is E466. Together with xanthan gum, they are the most commonly used and common thickeners in food applications.
Usually what we call CMC (in food) is its salt, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose or sodium CMC, not carboxymethyl cellulose itself.
Due to the poor water solubility of CMC, for better use, it is usually made into sodium salt. CMC sodium is a water-soluble cellulose ether obtained by chemical modification of natural cellulose such as cotton linter or wood pulp.
HOSEACHEM@carboxymethylcellulose sodium is often used in foods and beverages to make the food thick and creamy to attract the appetite of customers. It thickens and stabilizes many foods by maintaining moisture, keeping the oil and water phase components from separating and producing a consistent texture.
1. The production process of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose generally has two steps: alkalization and etherification.
1.1 Alkalization
Disperse the raw cellulose pulp in an alkali solution (usually sodium hydroxide, 5-50%) to obtain alkali cellulose.
Cell-OH+NaOH →Cell·O-Na+ +H2O
1.2 Etherification
The alkali cellulose is etherified with sodium monochloroacetate (up to 30%) in an alcohol-water medium. During this process, the mixture of alkali cellulose and reagent is heated (50–75°C) and stirred.
ClCH2COOH+NaOH→ClCH2COONa+H2O
Cell·O-Na+ +ClCH2COO- →Cell-OCH2COO-Na
2. the degree of substitution of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose DS:
The degree of substitution DS of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is the average number of hydroxyl groups substituted per glucopyranose unit. The number of hydroxyl groups is completely replaced. The degree of substitution is 3, which can be determined by the reaction conditions and the use of organic solvents (such as ethanol and isopropanol). To control. As the DS value increases, the transparency of the solution will increase accordingly. According to the European Union, the DS value of food-grade cellulose gum is 0.2-1.5 carboxymethyl (-CH2COOH) per anhydroglucose unit.
3. Solubility of Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose:
3.1 In the water
Degree of substitution (DS) and viscosity are the two main factors affecting its water solubility.
Form a viscous colloidal solution with water. Cellulose gum has good solubility in water and is easy to absorb water. When it is dissolved in cold or hot water, it forms a colloidal solution.
Generally, the viscosity is between 25 and 50000mPa.s, and it can be dissolved in alkali only when the DS value is less than 0.3. When the DS value is greater than 0.4, it is easily soluble in water, when the DS is close to 0.7, it is easily soluble in water, and when the DS is greater than 1, it is difficult to dissolve in water.
3.2 In organic solvents
It is insoluble in organic solvents such as methanol, ethanol, copper, chloroform and benzene.
4. Viscosity of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose:
Generally, the viscosity of the solution is related to the degree of polymerization of cellulose (DP), solution concentration, pH value, temperature, degree of substitution, etc.
4.1 DP
Depends on the source of the cellulosic material.
4.2 Concentration
The viscosity increases as the concentration of the solution increases.
4.3 pH
Generally, the viscosity of a 1% CMC sodium solution reaches its highest level at a pH range of 6.5 to 9.0. There is little change in viscosity between pH 9.0-11.0.
When PH<6, the viscosity drops rapidly and CMC begins to form. The process will be completed at pH ≌2.5.
When PH>9, the viscosity will decrease, and the initial decrease process will be slow with the increase of PH. When PH>11.5, the decrease speed will increase.
4.4 Temperature
The viscosity decreases with increasing temperature, but the viscosity increases after cooling. However, when the temperature rises to a certain level, a permanent viscosity reduction occurs. The higher the degree of substitution, the less the viscosity is affected by temperature.
5. Uses of Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose:
5.1 Food grade sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is mainly used as a thickener in our daily food. In terms of taste, it gives foods thicker and creamier characteristics, and it is more attractive to consumers than foods without it.
Generally, it is used as a thickener, suspending agent, emulsifier, stabilizer and film-forming agent in many foods such as beverages, baking, dairy products, dessert products and meat products.
In some food applications, it can also replace some other thickeners, such as guar gum, gelatin, agar, sodium alginate and pectin. According to different viscosities and meshes, applications are diverse.
The following are its main uses and functions:
Beverages: stabilize particles and improve taste.
Baking: Improve volume and texture, retain moisture and extend shelf life.
Dessert: retain the liquid in the hydrocolloid dressing, improve the taste and reduce syneresis.
Dairy products: Control the growth of ice crystals in ice cream, prevent syneresis and improve texture.
Meat: retain water and increase yield.
5.2 Cosmetics
According to the "European Commission Cosmetic Substance and Ingredient Information Database", cellulose gum acts as a binder, emulsion stabilizer, film former, masking agent and viscosity control agent in cosmetics and personal care products.
5.3 Toothpaste
Its function in toothpaste is to completely mix liquid and solid raw materials, so that the toothpaste has proper viscosity, brightness and smoothness when it is molded and flowed.
5.4 Other
Other uses such as oil drilling, detergent, papermaking, textile, mining, ceramics, etc.
6. Safety of Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose
The safety of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose as a food additive has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), European Food Safety Agency (EFSA), FAO/WHO Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) and other authorities.
6.1 U.S. Food and Drug Administration
When used in accordance with Good Manufacturing Practices in foods for human consumption, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is generally considered safe (GRAS).
Can be used in cheese, food seasonings, Art Sw Jelly & Fruit Jams and Froz Desserts as an anti-caking agent or free-flowing agent, desiccant, emulsifier or emulsifier salt, formulation aid, humectant, stabilizer or thickener Agent and thickener. (5) (6)
6.2 European Food Safety Agency
Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose (E466) is listed in Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 as an authorized food additive, and is classified as an "additive other than coloring and sweetener".
2017 safety re-evaluation
After conducting research on short-term and long-term toxicity, carcinogenicity, reproductive toxicity, etc., in 2017, EFSA concluded: “No digital ADI is required, and the reported use and use level will not have safety issues. E466
Authorized use and use level
It has obtained Quantum Satisfaction (QS) approval for almost all authorized food categories in the European Union.
Its applications are listed in Group I and listed separately by E 466. The following foods may contain:
Desserts, snacks, edible ice cubes, chewing gum
Vegetable oils, breakfast cereals, food supplements
Cream, dairy products, dried fruits and vegetables
Nut butter and nut butter, cocoa and chocolate products
Breads and rolls, fine bakery products, unripe and processed cheese
Sauces, soups and broths, meat products
drinks
6.3 British Food Standards Agency
Classified as "emulsifiers, stabilizers, thickeners and gelling agents".
6.4 Australia and New Zealand Food Standards
It is an approved ingredient in Australia and New Zealand, with the code 466.
6.5 Joint Expert Committee on Food Additives
Functional categories: food additives, emulsifiers, stabilizers, thickeners.
Acceptable daily intake: ADI set in 1989 "unspecified".
7. sodium carboxymethyl cellulose side effects
It is generally considered safe, but some people may be allergic or sensitive to it.
8. Frequently asked questions about sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
8.1 Is sodium carboxymethyl cellulose the same as cellulose?
The difference is that sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is modified cellulose.
8.2 Is it natural?
As mentioned above, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is not natural. Although the raw material cellulose comes from natural sources, it is synthesized through alkalization and etherification.
8.3 Is it halal?
Yes, it is generally regarded as halal food because it is allowed by Islamic law and meets the requirements of halal food.
8.4 Is it kosher?
Yes, this is kosher. Modified cellulose E466 meets all "kashruth" requirements and can be certified as kosher.
8.5 Does it contain dairy products?
No, it is not derived from or contains dairy products.