Stability mechanism of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose in dairy products
2021-11-06In food, as a thickener, stabilizer, dispersant, extender and solid agent, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is widely used as a stable dispersant in dairy products, fruit juices, chocolate, beverages and yogurt.
At present, there are more than 1,500 dairy companies in China, mainly located in Northeast, North China, Northwest, Shanghai, Beijing and other cities. From the internal structure of liquid milk, 299,300 tons of fermented milk, accounting for 21%; 875,700 tons of pasteurized milk, accounting for 61.45%; and 250,000 tons of UHT milk, accounting for 17.54%. Statistics show that in 2002, China’s total milk production was 12.5 million tons, dairy production increased by 26% over the previous year, and liquid milk production increased by 66%. Experts predict that China's dairy market will maintain a growth rate of 15% in the next few years, and the annual growth rate of liquid milk will reach 30%. However, in terms of per capita consumption of dairy products, it is currently only 7.3kg, compared with the world's per capita consumption of 100kg of dairy products, there is still huge room for development.
The stability of cellulose carboxymethylated products is positively related to the uniformity of substitution: the better the uniformity of substitution, the better the stability of the carboxymethylated products of cellulose; improving the process and appropriately increasing the degree of substitution can increase the carboxyl Substitution uniformity of methylated products. The stability of cellulose carboxymethylation products is negatively related to viscosity: the lower the viscosity, the better the stability of cellulose carboxymethylation products. Therefore, carboxymethylated products of cellulose with medium and low viscosity are often used in foreign food stabilizers.
On frozen desserts-ice cream-sugar water sorbet, carboxymethyl cellulose sodium CMC has good dispersibility, and can control the formation of ice crystals like other stabilizers, maintain a uniform and consistent tissue, even if it is repeatedly frozen-thawed, it can be maintained It is stable, and can give excellent taste when the dosage is small.
In low-fat ice cream and milk sorbet, sodium carboxymethyl cellulose CMC is mixed with about 15% carrageenan to prevent the separation of the mixture before freezing. As the fat content increases, the amount of CMC increases to obtain a smooth Structure; in frozen milk products, 2% CMC stabilizer can be added; in syrup, 0.75% ~1% CMC stabilizer can be added; plant substances can also be used to replace milk fat for artificial sweet foods, such as sorbus Sugar alcohol replaces the sugar in ice cream, and CMC is also used.
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose CMC is widely used in beverages, the purpose is to have good juice suspension, improve the taste and texture, eliminate the formation of oil rings at the bottleneck, and shelter the bad bitter taste of artificial sweets.
The addition of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose CMC to neutral milk can eliminate the syneresis of starch and carrageenan, and can also make whipped and foamed cream with stable storage; adding CMC to yogurt can be used when the protein is equal to pH. Point range reaction to form a soluble, storage-stable complex.
Sedimentation and slick oil are the most common quality problems in acidic milk beverages. Under low pH conditions, when the pH is close to the PI point, the casein micelles in dairy products will coagulate and precipitate. After dairy products are left for a long time, fat will float up and form a very unsightly collar. After adding stabilizers, the stabilizers and proteins form a non-ionic peptized complex system, which prevents the precipitation of casein and the amount of precipitation. It mainly depends on the stability of the system.
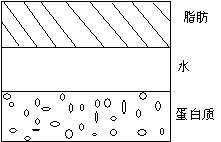
Separation and Floating
The molecular structure of the protein is as follows:
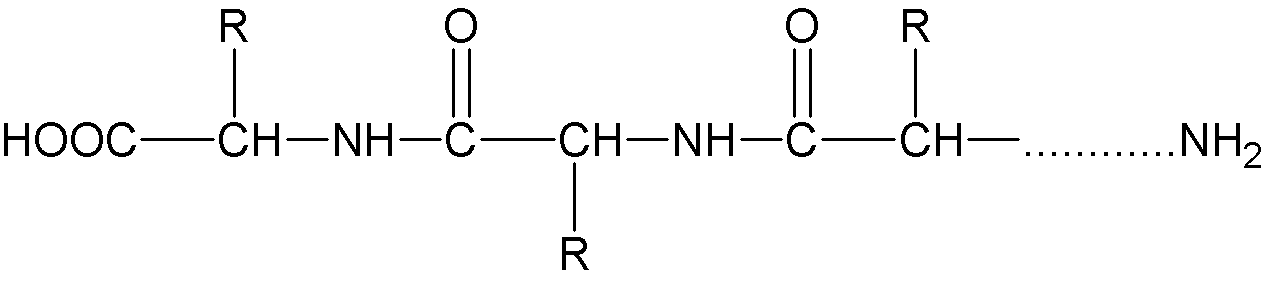
There are quite a lot of free amino and carboxyl groups in protein, forming zwitterions. Normally, proteins are positively charged in acidic solutions and negatively charged in alkaline solutions.
When the ionization degree of the amino group (-NH2) in the solution is equal to the ionization degree of the carboxymethyl group (-CH2COOH), the protein solution is neutral, and the pH value of the solution at this time is the isoelectric point PI of the protein.
When there is no stabilizer in the solution, when the pH value is close to the isoelectric point PI of the protein, the solution is the most unstable. It may be that the protein exhibits electrical neutrality to the outside and precipitates due to gravity.
Under certain pH conditions, the amino group (-NH2) in the protein reacts with H+ to form -NH3+.
Since carboxymethyl cellulose is anionic, it can peptize with ammonium salt through salt bonds and hydrogen bonds. Cellulose ether is a spatial network structure that stretches in the solution to fully disperse the protein and form a stable composite. structure.
Schematic diagram of the composite structure of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose CMC and protein
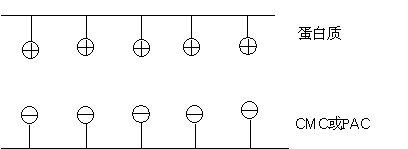
On the one hand, carboxymethyl cellulose peptizes with the ammonium salt in the protein to form a stable system, which prevents the aggregation of the protein and plays a role in stabilizing the protein;
On the other hand, carboxymethyl cellulose and protein form a stable non-ionic peptizing system, so that the solution has a certain emulsification effect.
The structure of fat (take triglycerides as an example)
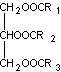
Fat is different from carbohydrates and proteins. It does not form long molecular chains and is insoluble in water. It is a non-ionic substance and is incompatible with ionic systems. It can only work with non-ionic systems.
The composite structure formed by CMC and the amino group in the protein has an emulsifying effect and acts as a surfactant. During the mixing operation, the fat balls are prevented from stirring out the milk particles, so that the food maintains a good flavor, concentration, and mouthfeel.
To increase the stability of the composite system of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose CMC and protein, you can start from the following points:
a. Improve the uniformity of polyanion distribution in the stabilizer aqueous solution when it is negatively charged, which needs to improve the uniformity of product substitution, and make CMC have better acid and salt resistance.
b. Increase the negative charge when the stabilizer aqueous solution is a polyanion. Increasing the degree of substitution of CMC is conducive to increasing the negative charge on CMC, which improves the stability of the CMC and protein composite system.