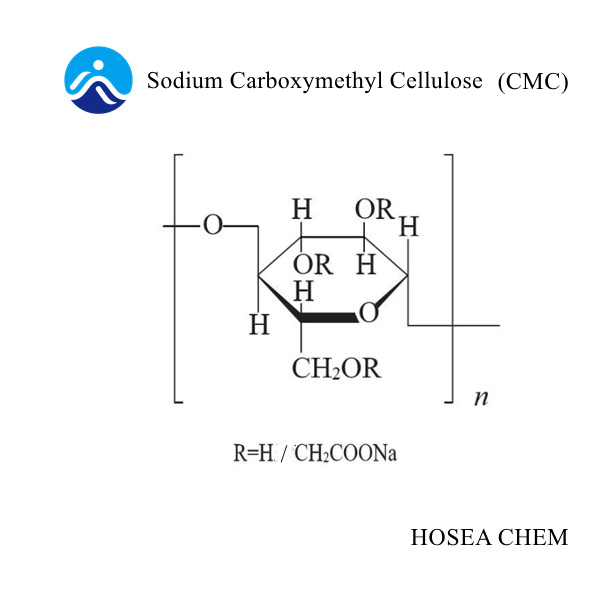
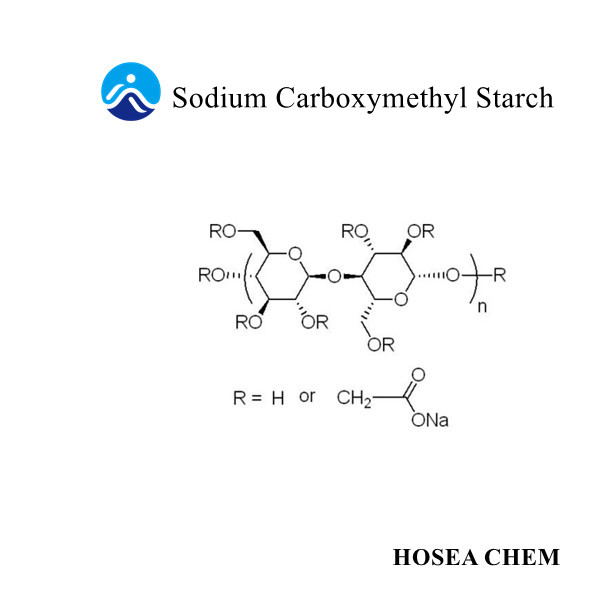
Properties of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose
2021-12-211. The equilibrium moisture of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose CMC increases with the increase of air humidity, and decreases with the increase of temperature. After reaching the equilibrium, it stops absorbing moisture.
2. The aqueous solution of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose has excellent adhesion, thickening, emulsification, suspension, film formation, limb protection, moisture retention, enzyme resistance and metabolic inertia.
3. The aqueous solution of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is connected to lead, iron, tin, silver, aluminum, copper and some heavy metals, and will form precipitation; for calcium, salt and other salts, it will not form precipitation, but it will reduce carboxymethyl cellulose The viscosity of sodium CMC aqueous solution; it can be mixed with water-soluble animal glue, glycerin, ethylene glycol, sorbitol, gum arabic and soluble starch and other aqueous solutions; it will precipitate acid carboxymethyl cellulose sodium CMC when it encounters acid.
4. The viscosity of the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution increases with the increase in the concentration of the solution, and their logarithmic values are approximately linear.
5. The viscosity of the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution decreases with the increase of temperature. The viscosity rises when it is cooled, but when the temperature rises to a certain level (the temperature limit is 50°C), a permanent viscosity decrease occurs. But the higher the substitution degree of CMC sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, the less the viscosity is affected by temperature. When the substitution degree is above 1.0, it is extremely stable.
6. The viscosity of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution is the largest and most stable when the pH value is 6.5-9.0. When pH<6, the viscosity drops rapidly and begins to form sodium carboxymethyl cellulose CMC acid, which is complete at pH=2.5; if pHl>9.0, the viscosity will also drop, which is relatively slow at first, but when pHl>11.5 At that time, it began to drop sharply.
7. The viscosity of the sodium carboxymethyl cellulose solution increases with the increase of the degree of polymerization, but it varies with the degree of substitution, and the relationship between the three must be considered.