Classification of cellulose ethers
2021-11-06Classification of cellulose ethers
There are many varieties of cellulose ethers, and they are still increasing. There are nearly a thousand varieties of cellulose ethers, which can be classified according to five different methods, namely:
①According to the viscosity of the standard aqueous solution
②According to the type of substituent
③According to the degree of substitution
④According to the physical structure (ionization)
⑤According to the solubility
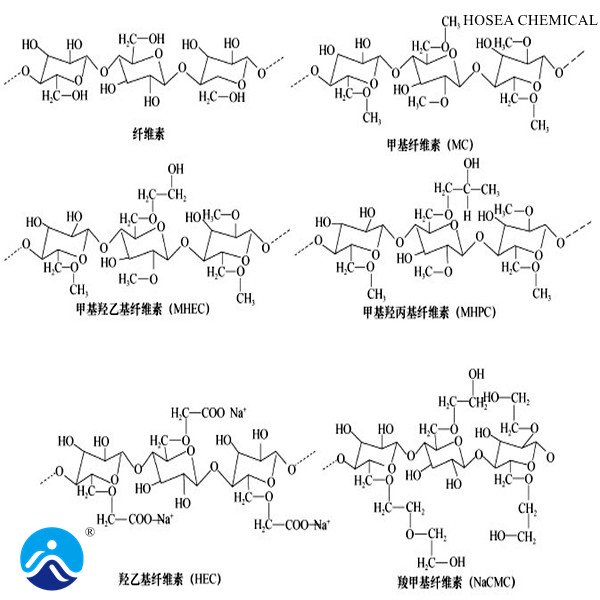
According to the types of substituents, cellulose ethers can be divided into single ethers and mixed ethers. There is only one type of substituent in a single ether. In the mixed ether, the cellulose ether molecular chain can have two or more substituents. Examples of main varieties are as follows:
1. Single ethers:
Methyl Cellulose (MC)
Ethyl cellulose (EC)
Hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC)
Cyanoethyl Cellulose (CEC)
2.Mixed ethers:
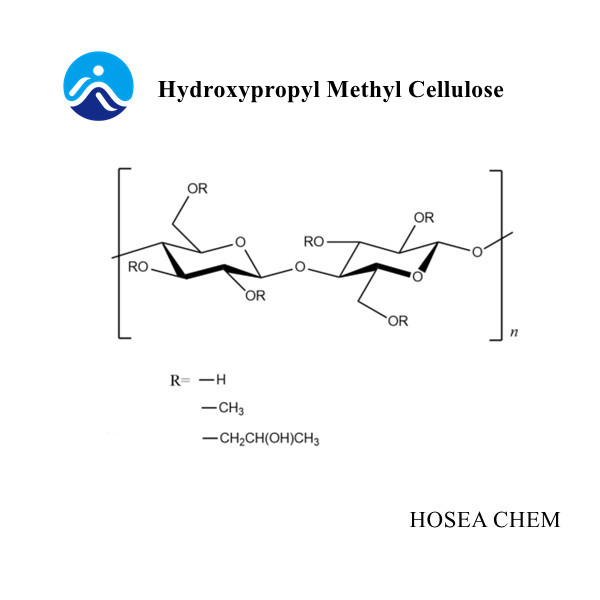
Hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC)
Methyl Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (MCEC)
Hydroxyethyl methyl cellulose (HEMC)
Carboxymethyl Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (CMHEC)
Carboxymethyl Hydroxypropyl Cellulose (CMHPC)
Carboxymethyl methyl cellulose (CMMC)
Carboxymethyl ethyl cellulose (CMEC)
Hydroxybutyl methyl cellulose (HBMC)
Ethyl Hydroxyethyl Cellulose (EHEC)
Ethyl Methyl Cellulose (EMC)
3.According to ionization:
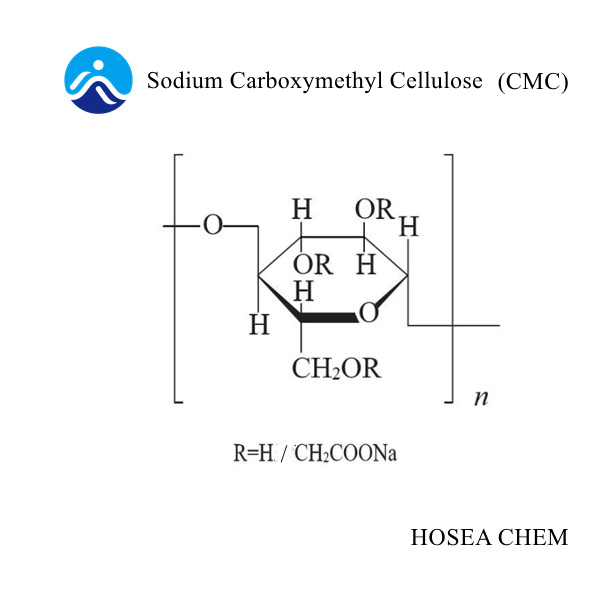
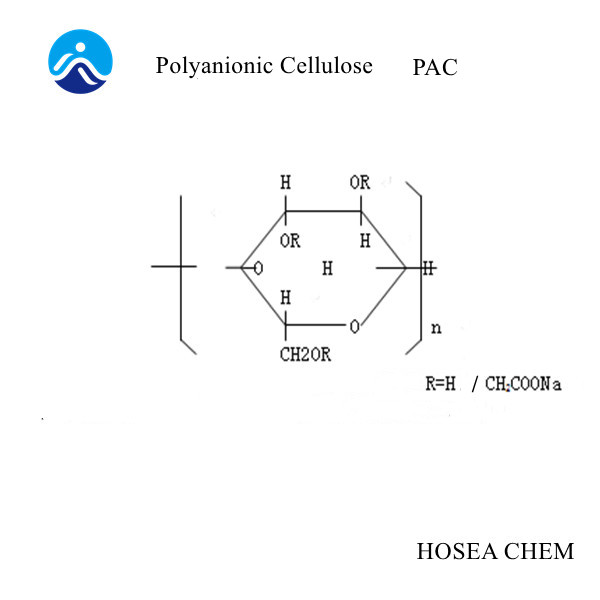
①Ionic ether, such as CMC, PAC
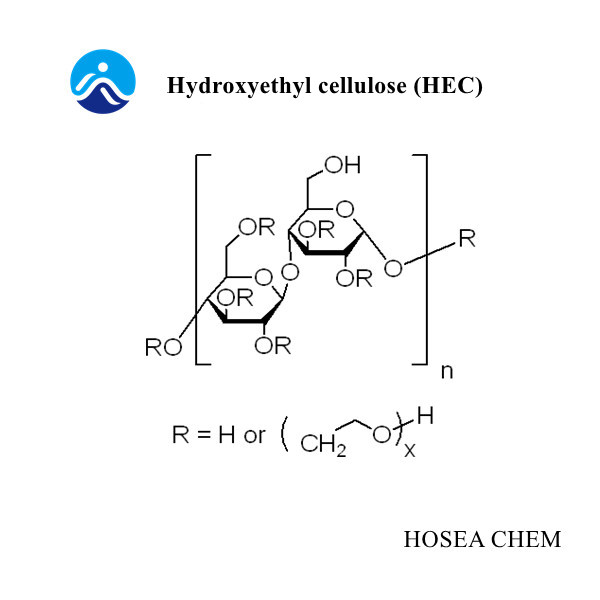
②Non-release ether, such as HPMC, MC, HPC, HEC
③Ionic and non-ionic mixed ethers, such as CMHEC, CMHPC, CMMC, CMEC
4. Divided into dissolution performance:
①Water-soluble fiber ether, HPMC, PAC, HEC, MC, HEMC, HPC, CMC
②Organic soluble cellulose ether, such as EC, CEC